How to Get started with Redis Today
June 2, 2017
What is a Redis? Why would I wanna use it today?
You might've asked those questions and if not I'll answer them for you anyway. The formal definition of Redis according to redis.io is...
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries.
Does it make sense yet? Maybe not. It didn't for me. Here's my explanation of what Redis is from the perspective of someone who would want to use it in a web framework such as Rails.
Redis is a super fast database that uses in-memory storage (aka RAM) to create caching and time critical functionality such as instant messaging. Redis supports many different types of data structures.
My definition is missing a few of the finer points but I feel like it gets the point across. So to sum things up Redis is a really fast database that uses key-value pairs to store and retrieve data. It is possible to use Redis alone but it is commonly used in tandem with other large databases since Redis is in-memory.
Finally, I'll address the why. For developers, it's mainly used for caching things such as views. I know for Rails specifically it's used for Action Cable and can be plugged in easily as the cache store. If neither of those things rings a bell that's fine because we won't be covering that today. To put it simply, Redis can make your website a lot faster. There is a much bigger picture though that is worth exploring. I hope you're still interested because we'll be downloading it next to start playing with it.
Downloading Redis
Downloading Redis is relatively easy if you have homebrew installed. If you have other requirements though you can follow their Download Instructions on their web site. If you're using macOS and have Homebrew installed (you can check by typing "brew" into the terminal) then just do the following in your terminal.
brew install redis
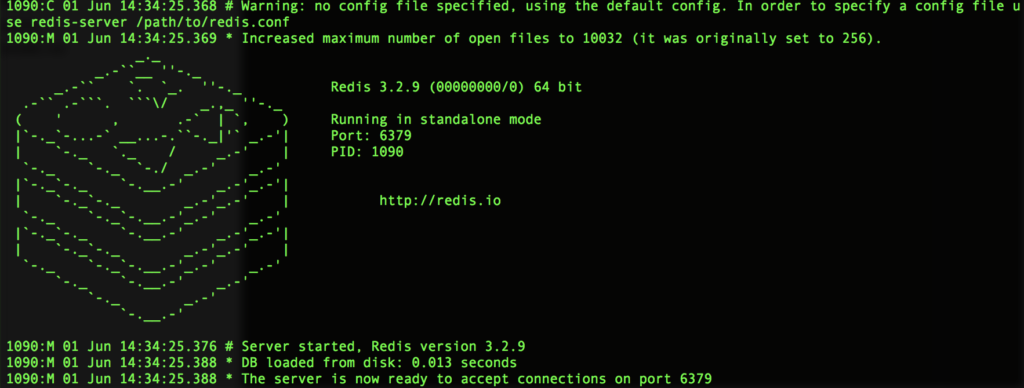
redis-serverThat'll install Redis on your machine and start the server. If that all worked right then you'll see an image like this in your terminal.
That's it for installing Redis. Next, we'll take a look at playing around with Redis in the command line tool.
Using Redis
With the Redis server still running you can enter the Redis's interactive command line interface by opening up another terminal window and typing the following.
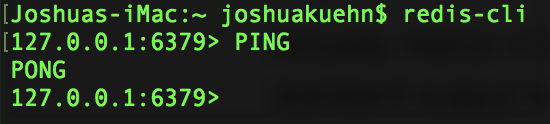
redis-cliThat'll open up the CLI in interactive mode and allow you to type commands to the server and it'll send back a reply. A common command to check if the server is running is to type in the command PING and it should reply with PONG.
Alternatively, you can pass commands after "redis-cli" to use it like traditional command line execution. If you exit the Redis CLI using control-c you can get the same PONG response if you type in the following to your terminal.
redis-cli pingPretty cool right! You have a lot of options to interact with the server but we'll play around inside the interactive console. With the server still running you can jump back in using "redis-cli" and we'll get started from there. Let's start by setting a simple key-value pair. We'll use English words as keys and the translated German words as the value.
set hello halloYou'll get back from the database a reply "OK" to let you know it successfully executed the command. If you want to check it though you can simply use the get command and supply the key to get back the value we set.
get helloYou'll receive back the value "hallo" hopefully. It's a really simple example but that's far from what all Redis can do. You can find a list of commands here on their website. If that doesn't seem impressive then I agree. Redis has built in their own benchmarking feature to show you better what it can handle.
Benchmarking Redis
Let's start by flushing the Redis database. We'll be using the redis-cli command line execution so just type in the following to remove all keys from all databases.
redis-cli flushallThat's to make sure we'll be benchmarking the same database together. Next, I want the database to execute one million set operations using a random key out of 100k possible keys. I found this particular test on the Redis website. They have plenty of others and they explain many other tests you can run to benchmark the database. Type in the following.
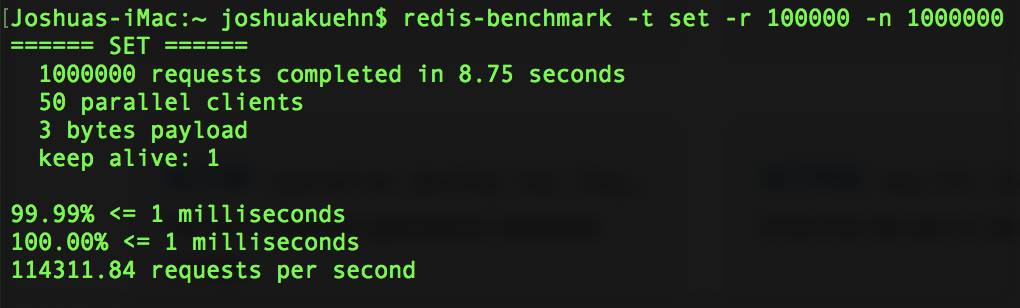
redis-benchmark -t set -r 100000 -n 1000000Once you type that in and press enter you'll see the database start working and then it'll give you a rundown of the performance. This will vary from machine to machine but here's what I got.
You can't tell me that servicing 114311 SET request in a second isn't impressive. This is just one of many utilities that Redis includes. If you'd like to see a rundown of the benchmark utility just go here and see what all it has to offer. I'm gonna show you one more feature of Redis called Pub/sub.
Pub/sub with Redis
This is probably my favorite feature of Redis. If you're scratching your head at the "Pub/sub" part then let me explain a little. That actually stands for "Publisher" and "Subscriber". It's a paradigm in software architecture that allows a publisher to send out messages and a subscriber to ask to receive those messages. Let me show you what I mean in redis-cli. Type in the following to your terminal.
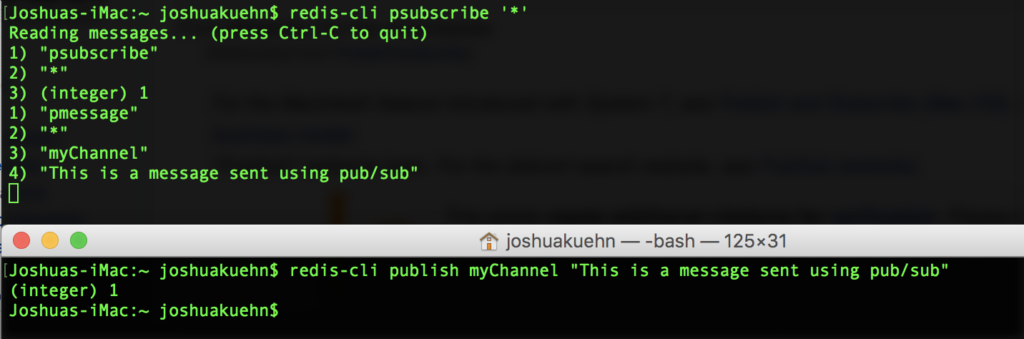
redis-cli psubscribe '*'In the pub/sub paradigm, we have something called "channels" which represent places that messages will be sent. The above command says we want to subscribe to all channels because the psubscribe command uses pattern matching to look for channels and the " * " command means match everything. That means we'll now receive any messages published on any channel. Now open up an additional terminal window and type this.
redis-cli publish myChannel "This is a message sent using pub/sub"This command will send out a message on the channel "myChannel" and the message will be "This is a message sent using pub/sub". If you have the subscribe terminal open and the publish one open it should look something like this.
You can see my top terminal was the subscriber. It displays information about what channel it received the message from and then what the message was. There are a few other key commands you can check out on the Redis site here. That feature is extremely powerful so use with care!
Rails and Redis
After all this, you might still wonder what the relevance of Redis is. It's hard to imagine until we plug it into something like Rails and observe what's going on. I'll be making an additional post on that later but for now, keep playing around with Redis. Feel free to ask me any questions below or hit me up on twitter @josh_qn.
Thanks for reading! If you found this helpful then please leave me a comment. If you didn't find it helpful then still leave a comment telling me what you thought it was missing.
Thanks again! Auf wiedersehen!